- Ye Shi
- Home
- About Me
- Research
- Publications
- Activities
- Group
Research
My current research interests mainly focus on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Smart Grids, and on the fundamental optimizations underlying them. I am interested in developing Responsible AI (RAI) algorithms that are more robust, more privacy-preserving and more explainable compared with traditional deep learning methods. Moreover, our target is to use the developed RAI methods to solve not only the tasks like Computer Vision and Natual Laguage Processing, but also the real-world applications, such as Smart Grid and Autonomous vehicles. Our undergoing research projects are as follows:
Optimization, Machine Learning and 3D Vision
Recent years have seen a variety of applications in machine learning that consider optimization as a tool for inference learning. Embedding optimization problems as optimization layers in deep neural networks can capture useful inductive bias, such as domain specific knowledge and priors. Our target is to connect the date-driven learning model and physics-driven optimization models in an end-to-end differentiable learning framework. Under this framework, the learning model will be more explainable and robust while the optimization model will be more time-efficient. 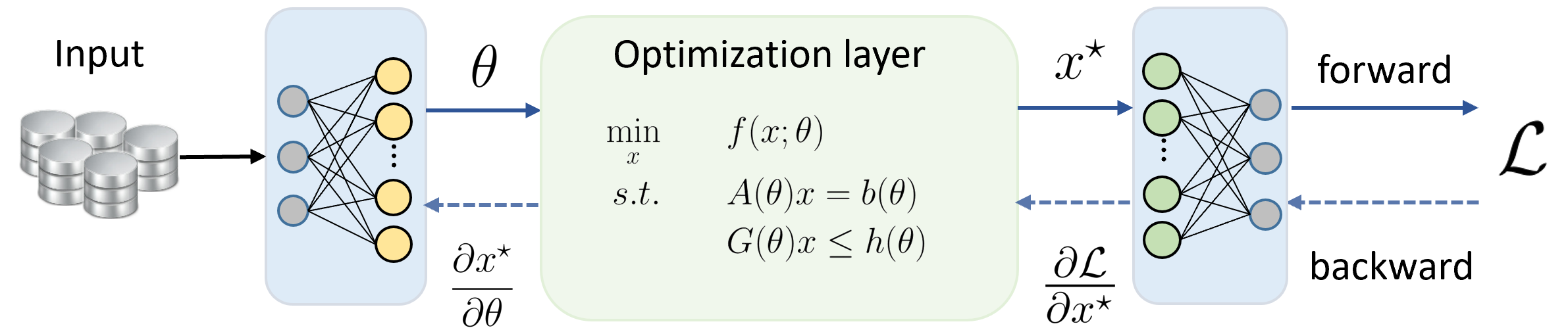 |
- [1] Haixiang Sun, Ye Shi*, Jingya Wang, Hoang Duong Tuan, H.V. Poor, Dacheng Tao, Alternating Differentiation for Optimization Layers, accepted by ICLR 2023.
- [2] Wanxing Chang, Ye Shi*, Jingya Wang*, Hoang Duong Tuan, Unified Optimal Transport Framework for Universal Domain Adaptation, accepted by NeurIPS 2022. (CCF A)
- [3] Juze Zhang, Jingya Wang*, Ye Shi*, Lan Xu, Fei Gao, Jingyi Yu, “Mutual Adaptive Reasoning for Monocular 3D Multi-Person Pose Estimation”, accepted by ACM MM 2022. (CCF A)
- [4] Juze Zhang, Ye Shi*, Yuexin Ma, Lan Xu, Jingyi Yu, Jingya Wang*, IKOL: Inverse kinematics optimization layer for 3D human pose and shape estimation via Gauss-Newton differentiation, accepted by AAAI 2023. (CCF A)
Federated Learning
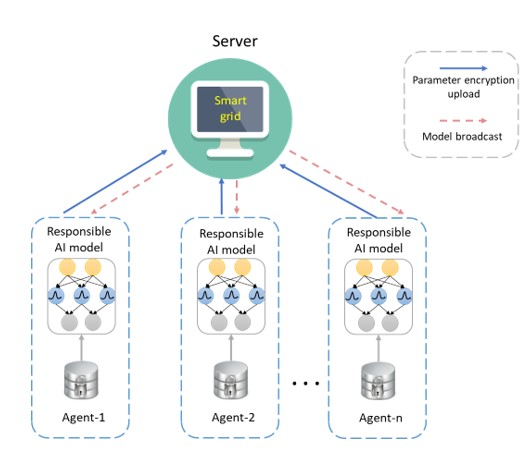 |
With the advent of the era of big data and artificial intelligence, data security has become an issue of increasing concern. The concept of federated learning has also emerged from data security: the essence of federated machine learning is a distributed machine learning framework, which makes full use of the data and computing power of multiple institutions to meet the requirements of user privacy protection and data security. Enable multiple parties to collaboratively build a general machine learning model, effectively solving the problem among multiple agents. This project aims to build a set of trustworthy federated learning algorithm framework and extend it to real-world applications, such as smart grids. Compared with the traditional federated learning algorithm in protecting data privacy, this federated learning framework will also take into account the robustness and reliability of the model. Many issues related to data security in the smart grid can be completed within this framework, such as distributed power flow optimization problems, large-scale electric vehicle charging and discharging coordination problems, and distributed demand response, etc. |
- [1] Ye Shi # , Leijie Zhang # , Zehong Cao, M. Tanveer and Chin-Teng Lin*, ”Distributed Semi-supervised Fuzzy Regression with Interpolation Consistency Regularization”, accepted by IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021. (SCI Q1, Impact Factor 12.029)
- [2] Leijie Zhang # , Ye Shi #* , Yu-Cheng Chang, and Chin-Teng Lin,” Hierarchical fuzzy neural networks with privacy preservation on heterogeneous big data”, IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 29, pp. 46 - 58, 2021. (SCI Q1, Impact Factor 12.029)
- [3] Ye Shi* , Chin-Teng Lin, Yu-Cheng Chang, Weiping Ding, Yuhui Shi and Xin Yao, "Consensus learning for distributed fuzzy neural network in big data environment", IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, vol. 5, pp. 29-41, 2021. (SCI Q1, Impact Factor 4.851)
- [4] Leijie Zhang, Ye Shi*, Yu-Cheng Chang and Chin-Teng Lin*, "Federated Fuzzy Neural Networks with Evolutionary Rule Learning", accepted by IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2022. (SCI Q1, Impact Factor 12.253)
- [5] Hongxia Li#, Zhongyi Cai#, Jingya Wang, Jiangnan Tang, Chin-Teng Lin, Ye Shi*, FedTP: Federated Learning by Transformer Personalization, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023 (SCI Q1, Impact Factor 14.225) .
Optimization and AI for Smart Energy
 |
Innovative breakthroughs in the new generation of smart grid and battery technology have promoted the vigorous development of electric vehicles (EVs). However, due to the large-scale popularity of EVs, the large-scale charging and discharging of EVs in smart grid may cause many potential effects, such as voltage fluctuations, load changes and power loss. There is relatively few work that can meet the needs of joint coordination between large-scale electric vehicle charging/discharging and optimal power flow (EV-OPF). Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop key technologies that can solve this problem. This project first establishes a dynamic optimization model for the large-scale EV-OPF problem and then designs a mixed-integer non-convex optimization algorithm to solve this problem. In order to tackle the uncertainty of EVs’ charging demand and time of arrival, a model predictive control model is developed. Taking into account the shortcomings of centralized algorithms in system robustness, computing and communication costs, and data privacy, this project aims to investigate non-convex distributed optimization algorithms suitable for this problem, and to study their convergence mechanisms. |
- [1] Ye Shi*, Hoang Duong Tuan, Andrey V. Savkin, Chin-Teng Lin, Jian Guo Zhu, H. Vincent Poor, ”Distributed model predictive control for joint coordination of demand response and optimal power flow with renewables in smart grid”, Applied Energy, 290, 2021. (SCI Q1, Impact Factor 9.746)
- [2] Ye Shi, Hoang Duong Tuan, Andrey V. Savkin, Trung Q. Duong* and H. Vincent Poor, ”Model Predictive Control for Smart Grids with Multiple Electric-Vehicle Charging Stations”, IEEE Transaction on Smart Grid, vol. 10, pp. 2127-2136, 2019. (SCI Q1, Impact Factor 10.486)